Respirable crystalline silica is a mineral so fine that it is able to lodge deep in the lungs, potentially causing silicosis long after the job has been completed. California has logged more than 230 confirmed silicosis cases and 14 deaths since 2019.
In 2024 alone, more than a quarter of California’s inspected engineered-stone shops were hit with stop-work orders, and fines reached five-figure territory for “routine” violations. Now the emergency rule that triggered those shutdowns is permanent—no sunset clause, no grace period, no excuses.
If you manage bids, schedules, or safety talks, you should adjust your work to the new permanent standard under the Title 8 CCR §5204 regulation.
Who Does the New Silica Standard Affect?
Worker protection from respirable crystalline silica is a serious requirement of Cal/OSHA safety standards. Section 5204 covers all general-industry operations where workers may be exposed to respirable crystalline silica and work with artificial stone (composite, engineered, or “quartz” materials) or natural stone > 10 percent silica by weight.
Exceptions:
- Construction (§1532.3), agriculture (§3436), and sorptive-clay processing remain under their own rules.
- Objective-data exemptions below the 25 µg/m³ action level still apply—but not to “High-Exposure Trigger Tasks” (HETTs), meaning any cutting, grinding, drilling, polishing, or cleanup that disturbs artificial stone (> 0.1 % silica) or high-silica natural stone.
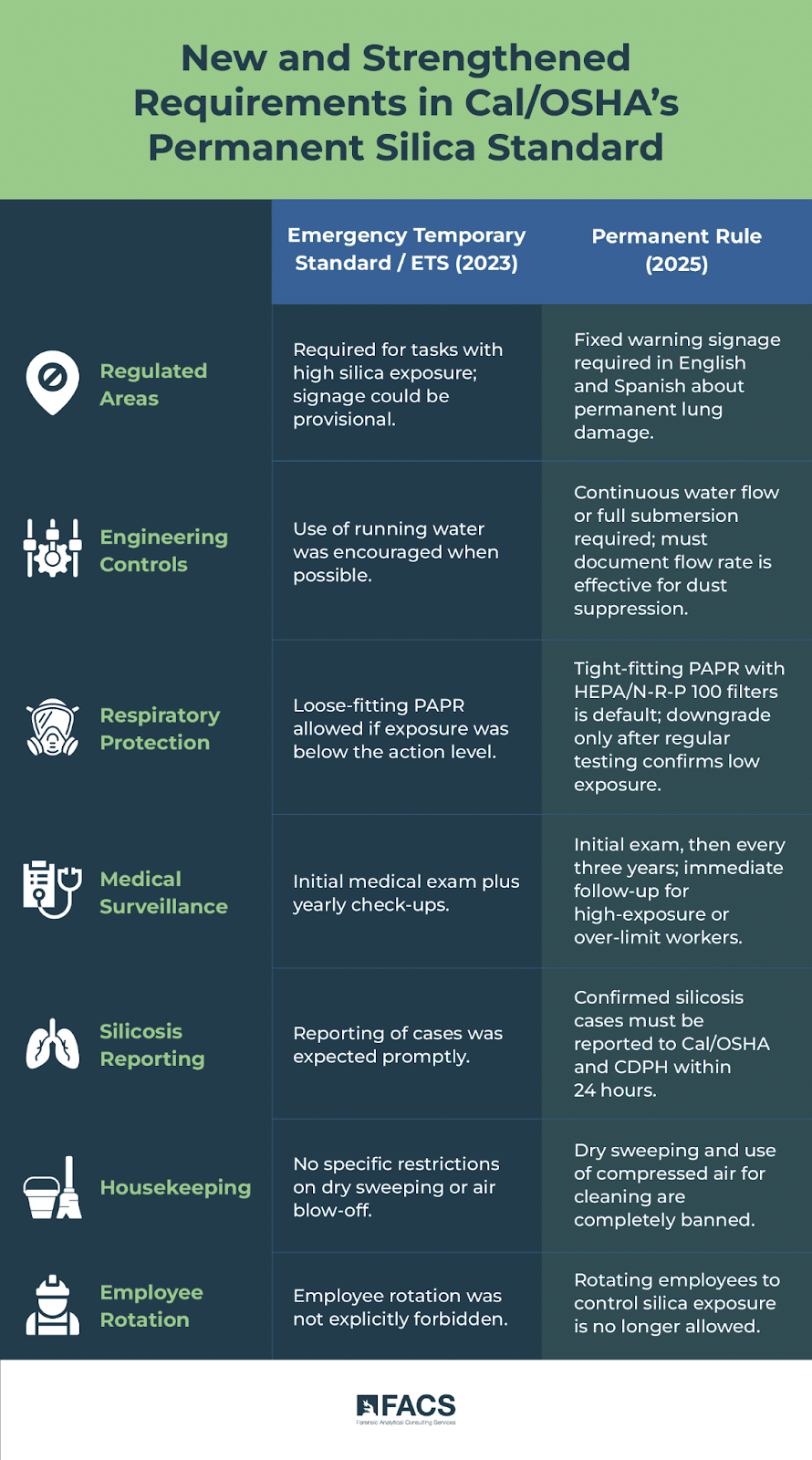
What Got Tougher in the Permanent Silica Standard
Regulated Areas:
ETS (2023): Required for high-exposure trigger tasks; provisional signage allowed.
Permanent Rule (2025): Signage text locked in—must warn of “permanent lung damage that may lead to death,” displayed in both English and Spanish.
Engineering Controls
ETS (2023): Running water “where feasible.”
Permanent Rule (2025): Continuous water flow or full submersion mandated; employer must document that flow rate is adequate for dust suppression.
Respiratory Protection
ETS (2023): Loose-fit PAPR allowed if exposure < Action Level.
Permanent Rule (2025): Tight-fit PAPR with HEPA/N-R-P 100 filters is the default; downgrade only after semi-annual sampling shows exposure < Action Level.
Medical Surveillance
ETS (2023): Baseline exam plus annual follow-up.
Permanent Rule (2025): Baseline, then every three years; immediate follow-ups required for high-exposure workers (HETT or > PEL results).
Silicosis Reporting
ETS (2023): “Prompt” reporting language.
Permanent Rule (2025): 24-hour deadline to notify Cal/OSHA and CDPH of any confirmed case.
Dry sweeping/air blow-off—banned outright.
Employee rotation—no longer an acceptable exposure control.
Eight Core Silica Exposure Duties for Employers
- Written Exposure-Control Plan – List all materials/tasks by silica content. Include air-monitoring records and engineering-control schematics.
- Exposure Assessment & Air Monitoring – Initial sampling plus 12-month repeat cycle; HETT work may trigger 6-month or 3-month cycles.
- Engineering Controls – Continuous-water tools, submerged cutting, water-jet, or local exhaust with HEPA filtration.
- Regulated-Area Management – Barricades or tape, plus bilingual danger signage.
- Respiratory-Protection Program – PAPR (HEPA/N100/R100/P100) minimum; fit-testing per §5144.
- Housekeeping Rules – Wet cleanup or HEPA vac only; no dry sweeping, no compressed-air blow-off.
- Medical Surveillance & Medical Removal Protection – Baseline exam, chest imaging as needed, and 3-year cycle; wage retention up to 6 months if removal required.
- 24-Hour Silicosis/Cancer Reporting & Recordkeeping – Confirmed cases reported within 24 hours; all sampling & medical records kept 30 years.
Penalties and Shut-Down Risk
Cal/OSHA’s 2025 penalty schedule caps a serious citation at $25,000 and a willful/repeat at $162,851. The minimum penalty for willful violations is $11,632.
But the real hammer is the Order Prohibiting Use (OPU). Inspectors spotting dry cutting or missing water-feed can tape off your saw on the spot. In 2024, more than a quarter of inspected shops were shut down until they fixed violations.
A Practical Roadmap to §5204 Compliance
Gap Analysis
- Map tasks where employees may be exposed against §5204 requirements
- Flag dry processes and inadequate water-feed tools.
Engineering Upgrades
- Budget for new wet saws, water-recycling systems, or downdraft HEPA tables.
- Verify flow rates meet manufacturer specs for dust suppression.
Engage a Qualified Person
- Exposure monitoring may have to be conducted by a third-party “qualified person,” such as a Certified Industrial Hygienist (CIH).
Finalize Written Exposure Control Plan & Training
- Implement exposure control plan
- Conduct bilingual, task-specific training; refresh annually.
Medical Program Contract
- Partner with an occupational clinic familiar with silicosis diagnostics and Cal/OSHA’s 24-hour reporting portal.
Frequently Asked Questions
“We’re below the Action Level—do we still need regulated areas?”
Yes, for any HETT. The regulated-area requirement is task-based, not exposure-based.
“Can I just rotate employees?”
No. Rotation is explicitly prohibited as an exposure control.
“Is a loose-fitting PAPR ever okay?”
Only if semi-annual sampling proves exposures < 25 µg/m³, and even then you need written justification and medical clearance.
The Bottom Line for California Employers Concerning Respirable Crystalline Silica Exposure
The engineered-stone sector is the immediate target, but any operation that liberates respirable crystalline silica is now under the microscope. Waiting for federal OSHA to act won’t help; California has already moved the goalposts.
However, the journey does not end with the enactment of stricter regulations; it continues with diligent compliance, robust enforcement, and the unwavering commitment of all stakeholders to safeguard the well-being of workers and communities.
The law is complex, but that isn’t a valid reason to ignore it. A good first step is to evaluate your high-exposure tasks. For help understanding the requirements and making sure your business is in compliance.
To speak with a FACS lead plan expert, call (888) 711-9998.